Maintenance
Warning
Failure to properly maintain the machine could result in premature failure of machine systems, causing possible harm to you or bystanders.
Keep the machine well maintained and in good working order as indicated in these instructions.
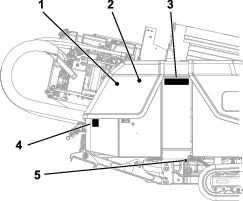
Note: Determine the left and right sides of the machine from the normal operating position. Place a service tag on the machine when maintenance procedures are being performed.Replace all covers and guards after you service or clean the machine. Do not operate the machine without the covers or guards in place.
Note: Download a free copy of the electrical or hydraulic schematic by visiting www.Toro.com and searching for your machine from the Manuals link on the home page.
Important: Refer to your engine owner’s manual for additional maintenance procedures.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule(s)
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| After the first 50 hours |
|
| After the first 100 hours |
|
| After the first 250 hours |
|
| Before each use or daily |
|
| Every 50 hours |
|
| Every 250 hours |
|
| Every 400 hours |
|
| Every 800 hours |
|
| Every 1,500 hours |
|
| Every 2,000 hours |
|
| Every 3,000 hours |
|
| Yearly or before storage |
|
| Every 2 years |
|
Warning
Improperly servicing or repairing the machine may cause injury or death.
If you do not understand the service procedures for this machine, contact your Authorized Service Dealer or see the service manual for this machine.
Warning
Operating the machine without covers and guards in place may cause personal injury or death.
Replace all covers and guards after you service or clean the machine. Do not operate the machine without the covers or guards in place.
Pre-Maintenance Procedures
Pre-Maintenance Safety
-
Before adjusting, cleaning, repairing, or leaving the machine, do the following:
-
Move the machine on a level surface.
-
Shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
Set the battery-disconnect switch to the OFF position.
-
Wait for all moving parts to stop.
-
Allow machine components to cool before performing maintenance.
-
-
If possible, do not perform maintenance while the engine is running. Keep away from moving parts.
-
Use adequate support to support the machine or components when required.
-
Carefully release pressure from components with stored energy.
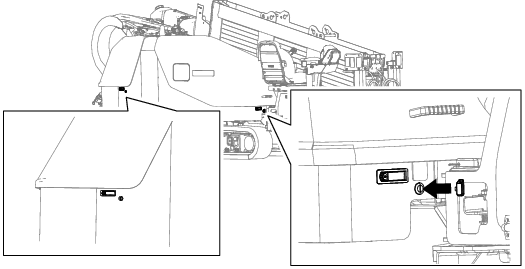
Accessing Internal Components
Opening the Front and Rear Hoods
Use 1 key to unlock the latch and push the lever open.
Use the smaller key to unlatch the hood.
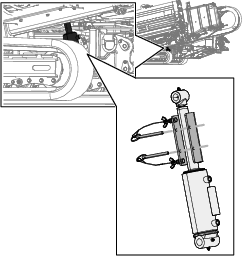
Using the Cylinder Lock
Warning
The thrust frame may lower when it is in the raised position, causing serious injury or death.
Install the cylinder lock before performing maintenance that requires the thrust frame to be raised.
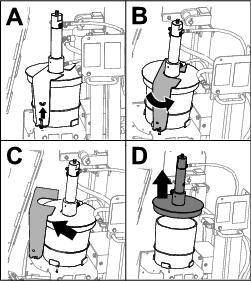
Installing the Cylinder Lock
-
Start the engine.
-
Lower the thrust frame to the fully-lowered position.
-
Shut off the engine.
-
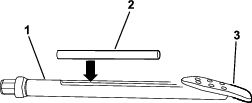
Position the cylinder lock over the cylinder rod (Figure 75).
-
Secure the cylinder lock with the cotter pin and clevis pin (Figure 75).
-
Turn the engine to the ON position, and raise the thrust frame until it rests on the cylinder lock.
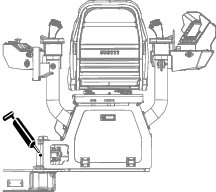
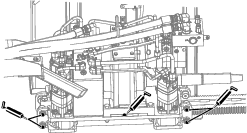
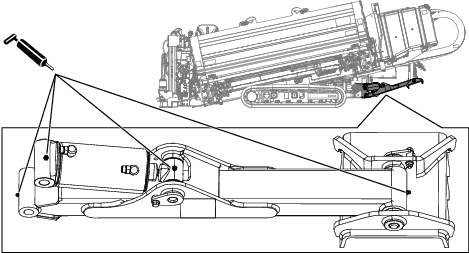
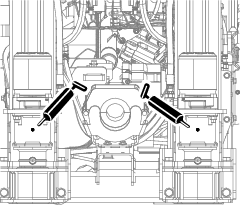
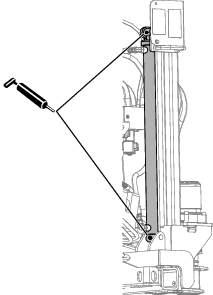
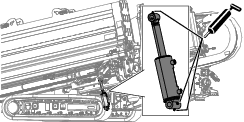
Lubrication
Greasing the Machine
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
Grease type: General-purpose grease.
Total number of grease fittings: 51
-
Clean the grease fittings with a rag.
-
Connect a grease gun to each fitting.
-
Pump grease into the fittings until grease begins to ooze out of the bearings (approximately 3 pumps).
-
Wipe up any excess grease.
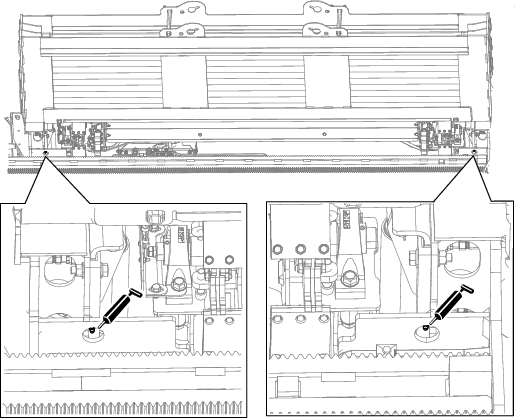
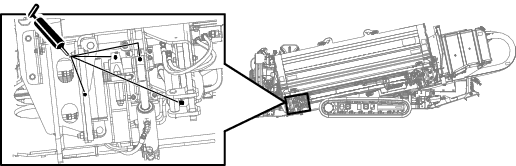
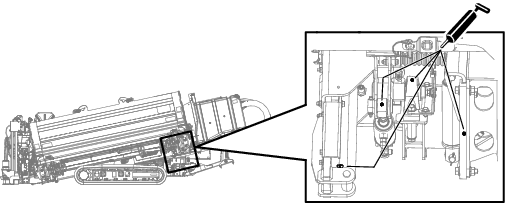
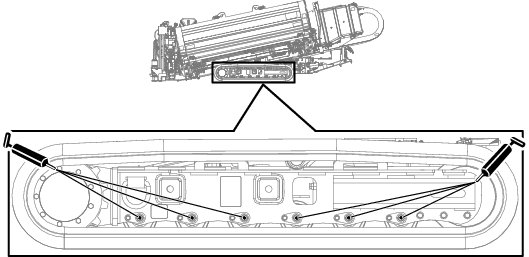
Engine Maintenance
Engine Safety
-
Shut off the engine before checking the oil or adding oil to the crankcase.
-
Do not change the governor speed or overspeed the engine.
Servicing the Air Cleaner
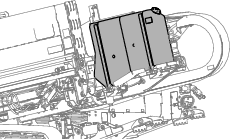
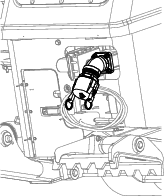
Check the air-cleaner body for damage that could cause an air leak and replace it if it is damaged. Check the entire intake system for leaks, damage, or loose hose clamps. Also, inspect the rubber intake-hose connections at the air cleaner and turbocharger to ensure that the connections are complete.
Service the air-cleaner filter only when the “Check Air Filter” message is displayed on the display; refer to the Software Guide for the machine. Changing the air filter before it is necessary only increases the chance of dirt entering the engine when you remove the filter.
Ensure that the cover is seated correctly and seals with the air-cleaner body.
Servicing the Air-Cleaner Cover
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 50 hours |
|
Check the air-cleaner body for damage that could cause an air leak. Replace a damaged air cleaner body.
Clean the air-cleaner cover (Figure 87).
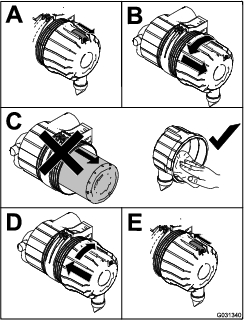
Servicing the Air-Cleaner Filter
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 250 hours |
|
The air-intake system on this machine is continuously monitored by an air-restriction sensor that displays when an advisory when to replace the air filter. Do not replace the elements until this occurs.
Important: Replace the secondary filter element only every 3 primary filter services. Do not remove the secondary element when cleaning or replacing the primary element. The inner element prevents dust from entering the engine when you service the primary element.
Important: Do not operate the engine without the air-cleaner elements, as this would allow foreign material to enter the engine and damage it.
-
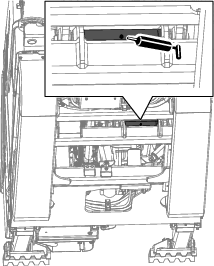
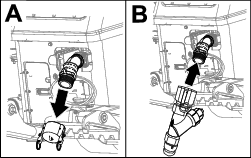
Release the latches securing the air-cleaner cover to the air-cleaner body (Figure 88).
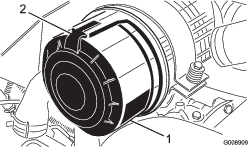
-
Remove the cover from the air-cleaner body.
-
Before removing the filter, use low-pressure air (275 kPa or 40 psi, clean and dry) to help remove large accumulations of debris packed between the outside of the primary filter and the canister.
Note: Avoid using high-pressure air that could force dirt through the filter into the intake. This cleaning process prevents debris from migrating into the intake when the primary filter is removed.
-
Remove the primary filter (Figure 89).
Note: Do not clean the used element due to the possibility of damage to the filter media.
Note: Replace the secondary filter every 3 primary filter services (Figure 90).
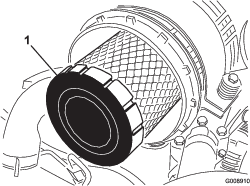
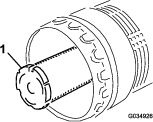
-
Inspect the new filter for shipping damage, checking the sealing end of the filter and the body.
Important: Do not use a damaged element.
-
Insert the new filter by applying pressure to the outer rim of the element to seat it in the canister.
Important: Do not apply pressure to the flexible center of the filter, as this may damage the filter.
-
Clean the dirt-ejection port located in the removable cover.
-
Remove the rubber outlet valve from the cover, clean the cavity, and replace the outlet valve.
-
Install the cover orienting the rubber outlet valve in a downward position—approximately between the 5 o’clock and 7 o’clock position when viewed from the end.
-
Secure the cover latches.
Servicing the Engine Oil
Crankcase Oil Capacity
11.2 L (11.8 US qt) with the filter
Oil Specification
Use high-quality, low-ash engine oil that meets or exceeds the following specifications:
-
API service category CJ-4 or higher
-
ACEA service category E6
-
JASO service category DH-2
Important: Using engine oil other than API CJ-4 or higher, ACEA E6, or JASO DH-2 may cause the diesel particulate filter to plug or cause engine damage.
Use the following engine oil viscosity grade:
-
Preferred oil: SAE 15W-40 (above 0°F)
-
Alternate oil: SAE 10W-30 or 5W-30 (all temperatures)
Toro Premium Engine Oil is available from your Authorized Service Dealer in either 15W-40 or 10W-30 viscosity grades. See the parts catalog for part numbers.
Checking the Engine-Oil Level
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
The engine is shipped with oil in the crankcase; however, the oil level must be checked before and after the engine is first started.
Important: Check the engine oil daily. If the engine-oil level is above the Full mark on the dipstick, the engine oil may be diluted with fuel;If the engine oil level is above the Full mark, change the engine oil.
The best time to check the engine oil is when the engine is cool before it has been started for the day. If it has already been run, allow the oil to drain back down to the sump for at least 10 minutes before checking. If the oil level is at or below the Add mark on the dipstick, add oil to bring the oil level to the Full mark. Do not overfill the engine with oil.
Important: Keep the engine oil level between the upper and lower limits on the dipstick; the engine may fail if you run it with too much or too little oil.
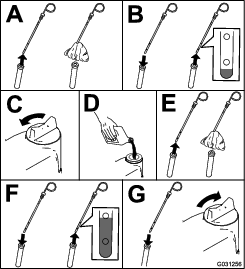
Check the engine-oil level as shown in Figure 91.
Changing the Engine Oil and Engine-Oil Filter
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| After the first 50 hours |
|
| Every 400 hours |
|
Note: Change the engine oil and filter more frequently when the operating conditions are extremely dusty or sandy.
-
Start the engine and let it run 5 minutes to allow the oil to warm up.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Change the engine oil as shown in Figure 93.
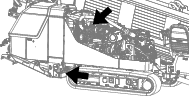
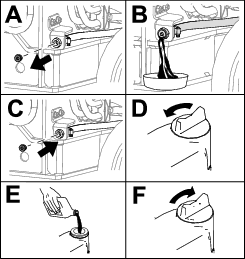
-
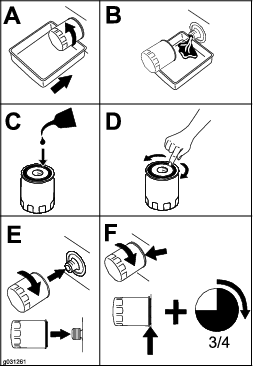
Change the engine-oil filter (Figure 94).
Note: Ensure that the oil-filter gasket touches the engine, and then an extra 3/4 turn is completed.
Adjusting the Engine-Valve Clearance
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Refer to your engine owner’s manual for the adjustment procedure.
Cleaning the Engine EGR Cooler
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 1,500 hours |
|
For information on cleaning the engine EGR cooler, refer to your engine owner’s manual.
Inspecting the Engine Crankcase-Breather System
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 1,500 hours |
|
For information on inspecting the engine crankcase-breather system, refer to your engine owner’s manual.
Checking and Replacing Fuel Hoses and Engine-Coolant Hoses
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 400 hours |
|
For information on checking and replacing fuel hoses and engine-coolant hoses, refer to your engine owner’s manual.
Lapping or Adjusting the Engine Intake and Exhaust Valves
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 2,000 hours |
|
For information on lapping or adjusting the engine intake and exhaust valves, refer to your engine owner’s manual.
Inspecting and Cleaning Engine-Emission-Control Components and Turbocharger
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 3,000 hours |
|
For information on inspecting and cleaning the engine-emission-control components, refer to your engine owner’s manual.
Fuel System Maintenance
Servicing the Fuel System
Draining the Fuel Tank
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Drain and clean the tank also if the fuel system becomes contaminated or if you are storing the machine for an extended period of time. Use clean fuel to flush out the tank.
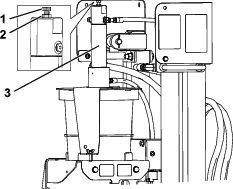
Servicing the Water Separator
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
| Every 400 hours |
|
Draining the Water Separator
-
Place a drain pan under the fuel filter.
-
Loosen the drain valve on the bottom of the filter (Figure 95).
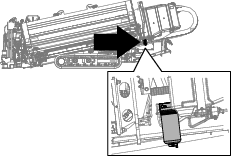
-
Tighten the valve after draining.
Replacing the Water-Separator Element
-
Place a clean container under the water separator.
-
Drain some fuel by loosening the vent plug and opening the drain valve (Figure 95).
-
Clean the area where the filter element mounts to the head.
-
Remove the filter element.
-
Apply a coating of clean fuel or engine oil to the new O-ring and element seal.
-
Install the new filter canister by hand until the gasket contacts the filter head, then tighten it an additional 1/2 turn.
Note: Do not use tools.
-
Close the drain plug.
-
With the vent plug still loosened, turn the key to the Run position (do not start the engine) so that the electric fuel pump can fill the new filter.
-
When fuel flows from the vent plug, close the vent plug, start the engine, and check for leaks.
Note: Correct as necessary with the engine off.
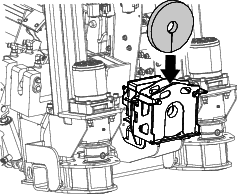
Replacing the Fuel Filter Element
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 400 hours |
|
-
Clean the area around the fuel-filter head (Figure 96).

-
Remove the filter and clean the filter-head-mounting surface (Figure 96).
-
Lubricate the filter gasket with clean, engine oil; refer to the engine owner's manual (included with the machine) for additional information.
-
Install the dry filter canister, by hand, until the gasket contacts the filter head, then rotate it an additional 1/2 turn.
-
Turn the key to the RUN position so that the electric fuel pump can fill the fuel-filter canister.
-
Start the engine and check for fuel leaks around the filter head.
Electrical System Maintenance
Battery Safety
-
Disconnect the battery before repairing the machine. Disconnect the negative terminal first and the positive last. Connect the positive terminal first and the negative last.
-
Charge the battery in an open, well-ventilated area, away from sparks and flames. Unplug the charger before connecting or disconnecting the battery. Wear protective clothing and use insulated tools.
Servicing the Battery
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 50 hours |
|
Warning
CALIFORNIA
Proposition 65 Warning
Use of this product may cause exposure to chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
Important: Before welding on the machine, disconnect the negative cable from the battery to prevent damage to the electrical system. Also, disconnect the engine and machine controllers before welding on the machine.
Note: Check the battery condition weekly or after every 50 hours of operation. Keep the terminals and the entire battery case clean because a dirty battery discharges slowly. To clean the battery, wash the entire case with a solution of baking soda and water. Rinse with clear water. Coat the battery posts and cable connectors with Grafo 112X (skin-over) grease (Toro Part No. 505-47) or petroleum jelly to prevent corrosion.
Warning
Exposure to battery acid or a battery explosion can cause serious personal injury.
Before you service a battery, wear face protection, protective gloves, and protective clothing.
Warning
A battery contains sulfuric acid, which can cause serious burns; and they can produce explosive gases.
-
Avoid contact with skin, eyes, or clothing; flush affected areas with water.
-
If taken internally, drink large quantities of water or milk. Do not induce vomiting. Seek medical attention immediately.
-
Keep sparks, flames, and lit cigarettes and cigars away from the battery.
-
Ventilate the battery when you are charging it or using it in an enclosed area.
-
Wear eye protection when working near a battery.
-
Wash your hands after handling a battery.
-
Keep the battery out of the reach of children.
Warning
If you try to charge or jump start a frozen battery, it could be explosive, causing personal injury to you or others in the area.
To prevent the battery electrolyte from freezing, keep the battery fully charged.
Warning
-
Sparks or a flame can cause hydrogen gas in a battery to explode.
-
When you disconnect the battery cables, disconnect the negative (-) cable first.
-
When you connect the battery cables, connect the negative (-) cable last.
-
Do not short-circuit the battery posts with a metal object.
-
Do not weld, grind, or smoke near a battery.
Note: The electrical system in this machine is 12 V.
Charging the Battery
Warning
Charging the battery produces gasses that can explode.
Do not smoke near the battery and keep sparks and flames away from battery.
Important: Keep the battery fully charged. This is especially important to prevent battery damage when the temperature is below 32° F (0° C).
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
Clean the exterior of the battery case and the battery posts.
Note: Connect the leads of the battery charger to battery posts before connecting the charger to the electrical source.
-
Look at the battery and identify the positive and negative battery posts.
-
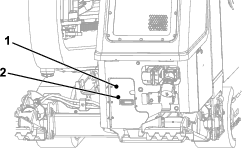
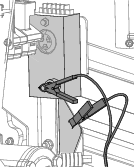
Connect the positive lead of the battery charger to the positive battery post (Figure 97).
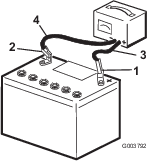
-
Connect the negative lead of the battery charger to the negative battery post (Figure 97).
-
Connect the battery charger to the electrical source.
Important: Do not overcharge the battery.
Note: Charge the battery a shown in battery charging table.
Battery-Charger Table
Charger setting Charging time 10 A 8 to 10 hours 20 A 4 to 6 hours (do not exceed 6 hours) -
When the battery is fully charged, unplug the charger from the electrical source, then disconnect the charger leads from the battery posts (Figure 97).
Jump-Starting the Machine
Warning
Jump-starting the battery can produce gasses that can explode.
Do not smoke near the battery and keep sparks and flames away from battery.
Note: This procedure requires 2 people to perform. Ensure that the person making the connections wears the proper face protection, protective gloves, and clothing.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
Ensure that all controls are in the NEUTRAL position.
-
Sit in the operator seat and have the other person make the connections.
Note: Ensure that the jumper battery is a 12-V battery.
Important: If you are using another machine for power, ensure that the 2 machines are not touching each other.
-
Prepare to start the engine; refer to Starting and Shutting Off the Engine.
-
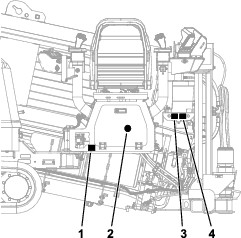
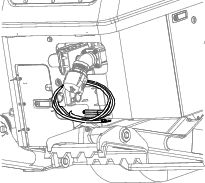
Remove the cover from the jump post (Figure 98).
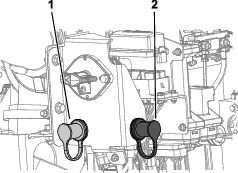
-
Connect the positive (+) jumper cable to the jump post (Figure 98).
-
Connect the negative (-) jumper cable to a ground point, such as an unpainted bolt or chassis member (Figure 98).
-
Start the engine; refer to Starting and Shutting Off the Engine.
Important: If the engine starts and then stops, do not operate the starter motor until the starter motor stops turning. Do not operate the starter motor for more than 30 seconds at a time. Wait 30 seconds before operating the starter motor to cool the motor and to build up the charge in the battery.
-
When the engine starts, have the other person disconnect the negative (-) jumper cable from the frame and then disconnect the positive (+) jumper cable (Figure 98).
Drive System Maintenance
Checking the Planetary Drive Oil Level Planetary Drive
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 50 hours |
|
Oil specification: SAE 85W-140 API classification level GL4
Planetary drive oil capacity: approximately 1.4 L (1.5 US qt)
Toro Premium Gear Oil is available from an Authorized Service Dealer. See the Parts Catalog for part numbers.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Clean the area around the oil-level plug with a cleaning solvent (Figure 99).
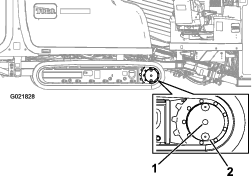
-
Rotate the planetary drive until the oil level and the oil-drain plugs are vertical to the ground (at the 6 o’clock position) as shown in Figure 99.
-
Remove the oil-level plug (Figure 99).
Note: The oil level is correct when it is up to the bottom of the oil-level plug hole.
-
If the oil is below the bottom of the hole, add the specified oil until the oil is level with the bottom of the hole.
-
Install and tighten the oil-level plug.
-
Repeat steps 1 through 6 to check the planetary-drive oil level on the other side of the machine.
Changing the Planetary Drive Oil
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| After the first 250 hours |
|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Note: Change the oil when it is warm, if possible.
-
Move the machine to a level surface.
-
Clean the area around the oil-level plug (Figure 99).
-
Rotate the planetary drive until the oil-drain plug is directly below the oil-level plug (Figure 99).
-
Shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
Place a drain pan under the oil-drain plug.
-
Remove the oil-level plug and the oil-drain plug.
-
Install the oil-drain plug.
-
Fill the track-drive planetary with oil until the oil is even with the bottom of the oil-level-plug hole.
-
Install the oil-level plug.
-
Repeat steps 1 through 9 to change the planetary-drive oil on the other side of the machine.
Checking the Rotary Gearbox Drive Oil
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Oil specification: SAE 85W-140 API classification level GL4
Rotary-gearbox drive oil capacity: approximately 2.7 L (5.75 US pt)
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Check the oil level on the sight-glass on the gearbox drive (Figure 100).
Note: The oil level should cover half of the sight-glass.
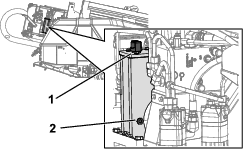
-
Remove the breather cap and add the oil into the gearbox drive until the oil level on the sight-glass is at least half full (Figure 100).
Changing the Rotary Gearbox Drive Oil
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| After the first 100 hours |
|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Note: Change the oil when it is warm, if possible.
-
Move the machine to a level surface and move the carriage all the way to the rear stop.
-
Shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
Remove the drain plug and drain the oil (Figure 101).
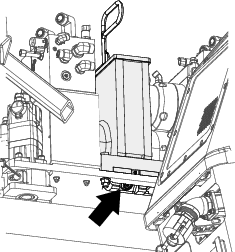
-
Install the drain plug.
-
Remove the breather cap (Figure 102).
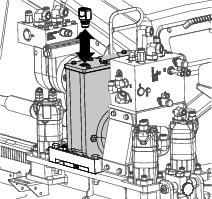
-
Fill the gearbox with oil until the oil level in the sight glass is more than half full (Figure 100).
-
Install the breather cap (Figure 102).
Servicing the Tracks
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
Warning
If you remove the track-tension grease valve found in the hydraulic-track tensioner or loosen it too much, grease can be released and may cause serious injury or death.
Grease in the hydraulic track is highly pressurized; ensure that the track-tension grease valve is not loosened more than 1 revolution at a time.
Tightening the Track Tension
If the track seems loose, tighten the track tension as follows:
-
Move the machine to a level surface and raise the thrust frame and stabilizers so that the tracks are raised.
-
Shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
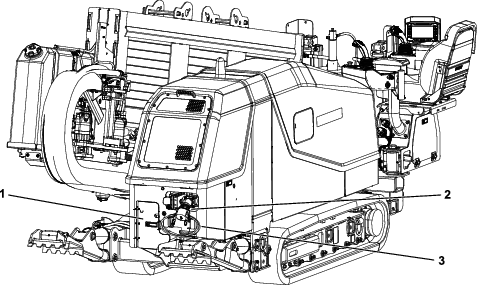
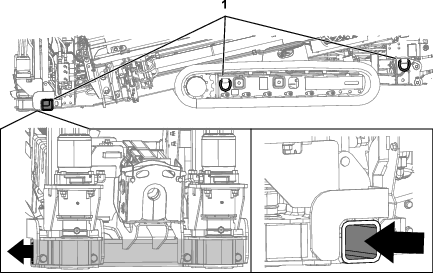
Remove dirt and debris found around the track-tension grease valve (Figure 103).
Important: Ensure that the area surrounding the track-tension grease valve is clean before beginning to adjust the track tension.
-
Remove the retaining bolts and cover that house the track-tension grease valve.
-
Apply grease to the fitting until the tension reaches 22,063 kPa (3,200 psi) as shown in Figure 103.
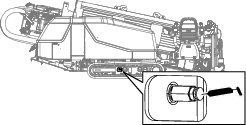
-
Remove excess grease from around the valve.
-
Install the cover and retaining bolts.
-
Repeat steps 3 through 7 to tighten the track tension on the other side.
Loosening the Track Tension
If the track seems tight, loosen the track tension as follows:
-
Move the machine to a level surface and raise the thrust frame and stabilizers so that the tracks are raised.
-
Shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
Remove dirt and debris found around the track-tension grease valve (Figure 103).
Important: Ensure that the entire area surrounding the track-tension grease valve is clean before beginning to adjust the track tension.
-
Remove the retaining bolts and cover that house the track-tension grease valve.
-
Turn the track-tension grease valve counterclockwise no more than 1 revolution (Figure 103).
Note: A 1-revolution turn releases grease and loosens the track.
-
When the tension reaches 3,200 psi, turn the track-tension grease valve clockwise to tighten it.
-
Remove excess grease from around the valve.
-
Install the cover and retaining bolts.
-
Repeat steps 3 through 8 to loosen the track tension on the other side.
Cooling System Maintenance
Coolant specification: 50/50 solution of ethylene-glycol antifreeze and water or equivalent
Engine and Radiator coolant capacity: 16.77 L (17.7 US qt)
Warning
If you remove the radiator cap from a hot engine, hot coolant could spray, causing scalding.
-
Wear face protection when opening the radiator cap.
-
Allow the cooling system to cool down to below 50°C (120°F) before removing the radiator cap.
-
Follow the instructions for checking and maintaining the engine cooling system.
Warning
Coolant is toxic.
-
Keep coolant away from children and pets.
-
If you are not using the same coolant again, dispose of it according to local environmental regulations.
Cooling System Safety
-
Swallowing engine coolant can cause poisoning; keep it out of reach of children and pets.
-
Discharge of hot, pressurized coolant or touching a hot radiator and surrounding parts can cause severe burns.
-
Always allow the engine to cool at least 15 minutes before removing the radiator cap.
-
Use a rag when opening the radiator cap, and open the cap slowly to allow steam to escape.
-
Checking the Coolant Level in the Reservoir
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
Important: Do not remove the radiator filler cap during this procedure.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Allow the engine to cool.
-
Open the front hood.
-
Check the coolant level in the reservoir (Figure 104).
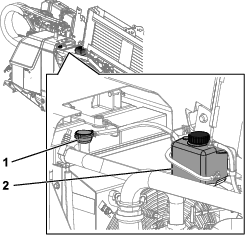
-
Add the specified coolant until the coolant level is 1/2 the reservoir capacity.
Note: Ensure that the coolant solution is thoroughly mixed before filling the reservoir.
Checking the Coolant Level in the Radiator
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 50 hours |
|
Warning
If the engine has been running, the radiator will be pressurized and the coolant inside will be hot. If you remove the cap, coolant may spray out, causing severe burns.
-
Do not remove the radiator cap to check coolant levels.
-
Do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool for at least 15 minutes or until the radiator cap is cool enough to touch without burning your hand.
Note: The cooling system is filled with a 50/50 solution of water and ethylene-glycol antifreeze.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Allow the engine to cool.
-
Open the front and rear hood.
-
Remove the radiator cap from the filler neck of the radiator and check the coolant level (Figure 104 and Figure 105).
Note: The coolant should be up to the filler neck.

-
If the coolant level is low, add coolant until the level is up to the bottom of the filler neck (Figure 105).
Important: Do not overfill the radiator.
Note: If the radiator coolant level is low and the coolant reservoir level is at the Full mark, check for air leaks in the hose between the radiator and the coolant reservoir.
-
Install the radiator filler cap, ensuring that it is tightly sealed (Figure 105).
-
If the air temperature is below 0°C (32°F), mix the ethylene glycol and water completely by running the engine at operating temperature for 5 minutes.
Checking the Condition of the Cooling-System Components
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 400 hours |
|
Check the condition of the cooling system for leaks, damage, dirt, and loose hoses and clamps. Clean, repair, tighten, and replace the components as necessary.
Checking the Concentration of the Coolant
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Test the concentration of ethylene glycol-based antifreeze in the coolant. Ensure that the coolant has a 50% ethylene glycol and 50% water mixture or equivalent.
Note: A 50% ethylene glycol and 50% distilled water mixture will protect the engine to -37° C (-34° F) throughout the year.
Using a concentration tester, check the concentration of the coolant mixture to ensure that it is 50% ethylene glycol and 50% distilled water or equivalent; refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for testing.
Cleaning the Cooling System
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Draining the Coolant from the System
Important: Do not pour coolant onto the ground or into an unapproved container that can leak.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Allow the engine to cool.
-
Open the front hood.
-
Remove the radiator cap (Figure 105).
-
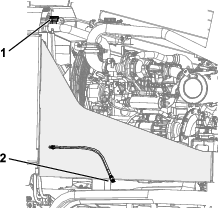
Place a drain pan under the drain plug (Figure 106).
Note: The coolant capacity of both the engine and the radiator is 16.8 L (17.7 US qt).
-
Open the radiator drain plug and allow the coolant system to drain completely.
Note: Dispose of the used coolant properly according to local codes.
-
Clean the threads on the drain plug and apply 3 layers of PTFE sealing tape.
-
Close the drain plug (Figure 106).
Flushing the Cooling System
Engine and radiator coolant capacity: 16.8 L (17.7 US qt)
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Condition the cooling system as follows:
-
Ensure that the coolant is drained from the radiator and that the drain plug is closed; refer to Draining the Coolant from the System.
-
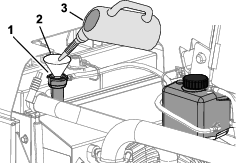
Add a cooling system cleaning solution to the radiator through the filler neck (Figure 107).
Note: Use cleaning solution of 21 g (12 oz dry) of sodium carbonate for every 17 L (18 US qt) of water; otherwise, use a commercially available equivalent. Follow the directions that come with the cleaning solution.
-
Close the drain plug (Figure 106).
Important: Do not install the radiator cap.
-
Operate the engine for 5 minutes or until the coolant temperature indicates 82° C (180° F), and then shut off the engine.
Caution
The cleaning solution is hot and can cause burns.
Stay away from the discharge end of the coolant drain.
-
Open the drain plug for the radiator, and drain the cleaning solution into a drain pan.
-
Clean the threads on the drain plug and apply 3 layers of PTFE sealing tape.
-
Close the drain plug.
-
-
Flush the cooling system as follows:
-
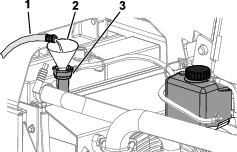
Open the filler-neck cap.
-
Fill the radiator with clean water (Figure 108).
-
Close the filler-neck cap.
-
Operate the engine for 5 minutes or until the coolant temperature indicates 82°C (180°F), and then shut off the engine.
Caution
The water is hot and can cause burns.
Stay away from the discharge end of the coolant drain plug.
-
Open the drain plug and drain the water into a drain pan.
-
Clean the threads on the drain plug and apply 3 layers of PTFE sealing tape.
-
If the water drained from the radiator is dirty, perform steps 3-1 through 3-5 until the water drained from the radiator is clean.
-
Close the drain plug (Figure 106).
-
Filling the System with Coolant
Important: You must fill the cooling system properly to prevent air pockets in the cooling passages. Failing to vent the cooling system properly can severely damage the cooling system and engine.
Important: Use a mixture of 50% ethylene glycol and 50% water mixture or equivalent in the machine. The lowest ambient operating temperature for this mixture is above -37° C (-34° F). If the ambient temperature is lower, adjust the mixture. Use a mixture of ethylene glycol and water or equivalent in the machine all year.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Remove the radiator cap (Figure 105).
-
Fill the radiator with coolant until the fluid level is up to the bottom of the filler neck (Figure 109).
Note: The coolant capacity of both the engine and the radiator is 16.8 L (17.7 US qt).

-
Install the radiator cap (Figure 105).
-
Fill the coolant reservoir with coolant until it is full.
-
Install the coolant reservoir cap.
-
Start the engine and run it at half throttle for 5 minutes.
-
shut off the engine and remove the key.
-
Wait 30 minutes, then check the fluid level in the coolant reservoir. If it is low, add coolant.
Belt Maintenance
Servicing the Engine-Drive Belt
Warning
Contacting a rotating belt can cause serious injury or death.
Shut off the engine and remove the key before working near belts.
Checking the Condition of the Belt
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 250 hours |
|
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
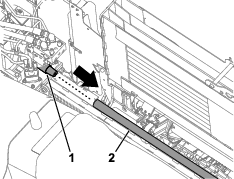
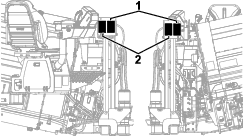
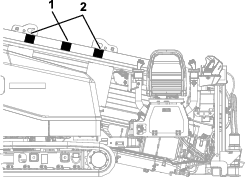
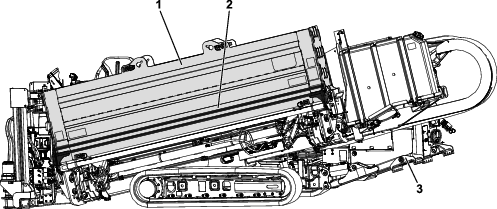
Inspect the belt for cuts, cracks, loose cords, grease, oil, twisting, or signs of abnormal wear (Figure 110).
Note: Replace the belt if it is excessively worn or damaged.
Checking the Belt Tension
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
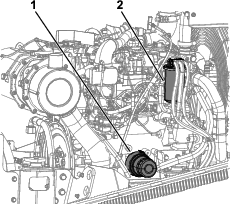
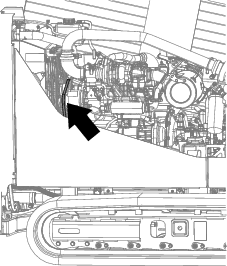
Align a straight edge over the drive belt and across the pulleys (Figure 110).
-
Push the belt down at the midway point between the fan pulley and the alternator pulley as shown in Figure 110.
Note: The range of belt deflection between the straight edge and the belt should be 7 to 9 mm (0.28 to 0.35 inches), under a load of 10 kg (22 lb).
-
If the tension of the belt is above or below the specified range, adjust the drive belt tension; refer to Adjusting the Tension of the Belt.
Adjusting the Tension of the Belt
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
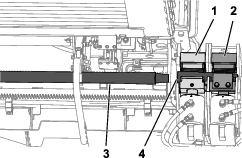
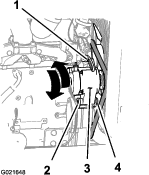
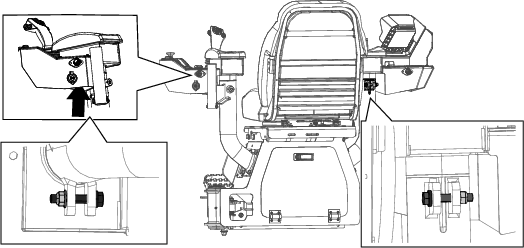
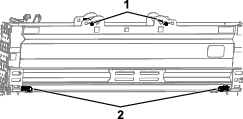
Loosen the nut and bolt at the pivot point for the alternator (Figure 111).
-
Loosen the adjustment bolt on the alternator (Figure 111).
-
Move the alternator away from the engine to increase the belt tension; move the alternator toward the engine to decrease the belt tension (Figure 111).
-
Tighten the alternator adjustment bolt (Figure 111).
-
Check the tension of the belt; refer to Checking the Belt Tension.
-
If the belt tension is correct, tighten the nut and bolt at the pivot point for the alternator (Figure 111); otherwise repeat steps 4 through 7.
Hydraulic System Maintenance
Hydraulic System Safety
-
Seek immediate medical attention if fluid is injected into skin. Injected fluid must be surgically removed within a few hours by a doctor.
-
Ensure that all hydraulic-fluid hoses and lines are in good condition and all hydraulic connections and fittings are tight before applying pressure to the hydraulic system.
-
Keep your body and hands away from pinhole leaks or nozzles that eject high-pressure hydraulic fluid.
-
Use cardboard or paper to find hydraulic leaks.
-
Safely relieve all pressure in the hydraulic system before performing any work on the hydraulic system.
Servicing the Hydraulic Fluid
The hydraulic reservoir is filled at the factory with approximately 102 L (27 US gallons) of high-quality hydraulic fluid. Check the level of the hydraulic fluid before the engine is first started and daily thereafter. The recommended replacement fluid follows:
Toro Premium All Season Hydraulic Fluid (Available in 5 gallon pails or 55 gallon drums. Contact your Authorized Service Dealer for part numbers.)
Alternate fluids: If the Toro fluid is not available, other fluids may be used provided they meet all the following material properties and industry specifications. We do not recommend the use of synthetic fluid. Consult with your lubricant dealer to identify a satisfactory product.
Note: Toro will not assume responsibility for damage caused by improper substitutions, so use only products from reputable manufacturers who will stand behind their recommendation.
| Material Properties: | ||
| Viscosity, ASTM D445 | 42.2 cSt at 40° C (104° F) | |
| 7.8 cSt at 100° C (212° F) | ||
| Viscosity Index ASTM D2270 | 158 | |
| Pour Point, ASTM D97 | -6° C (-42° F) | |
| Industry Specifications: | Vickers I-286-S (Quality Level), Vickers M-2950-S (Quality Level), Denison HF-0 | |
Note: Many hydraulic fluids are almost colorless, making it difficult to spot leaks. A red dye additive for the hydraulic fluid is available in 20 mL (2/3 oz) bottles. One bottle is sufficient for 15-22 L (4-6 gallons) of hydraulic fluid. Order the hydraulic oil from your Authorized Service Dealer.
Note: If ambient operating temperatures exceed 43° C (110° F), contact Toro for fluid recommendations.
Checking the Hydraulic Fluid
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
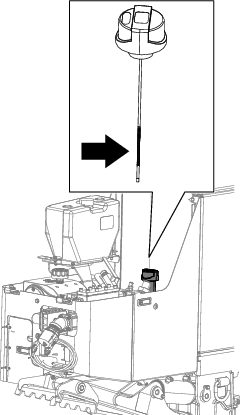
Check the hydraulic fluid as follows:
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Wait 10 minutes to allow the engine to cool and the hydraulic oil to stabilize.
-
If the level is low, open the hydraulic-tank cap, add a small amount of oil and wait 2 minutes for the oil level to stabilize.
Note: The oil level is between 1/2 to 2/3 full when the oil is at ambient temperature or if the engine has not yet been started for the day.
-
Continue to add the appropriate fluid in small increments until it reaches the top of the filler neck.
-
Install the cap onto the filler neck.
Changing the Hydraulic-Fluid Return Filter
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
-
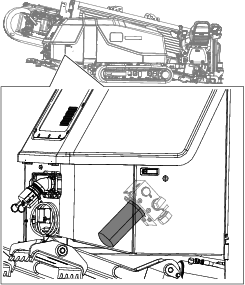
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Discard the old hydraulic-fluid return filter.
-
Install a new hydraulic-fluid return filter.
Changing the Hydraulic-Charge Filter
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
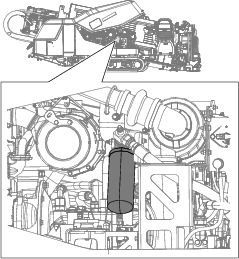
Place a drain pan under the filter.
-
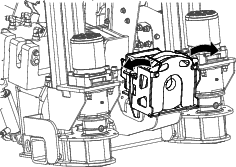
Using a filter wrench, remove the hydraulic-charge filter (Figure 114).
-
Discard the old filter.
-
Apply a thin layer of hydraulic oil to the o-ring of the filter.
-
Install and tighten the new filter with a filter wrench.
-
Start the engine, let it run idle for approximately 1 minute, then check for leaks around the hydraulic-charge filter.
Changing the Hydraulic Fluid
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 800 hours |
|
Important: If the fluid becomes contaminated, contact your Authorized Service Dealer, because the system must be flushed. Contaminated fluid looks milky or black when compared to clean oil.
Important: Use of any other filter may void the warranty on some components.
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the front hood.
-
Raise the machine using proper equipment.
Warning
Raising the rear of the machine relying solely on mechanical or hydraulic jacks could be dangerous. The mechanical or hydraulic jacks may not be enough support or may malfunction allowing the machine to fall, which could cause injury or death.
-
Do not rely solely on mechanical or hydraulic jacks for support.
-
Use adequate jack stands or equivalent support.
-
-
Place a large draining container under the hydraulic fluid tank.
-
Remove the drain plug from the bottom of the tank (Figure 115).
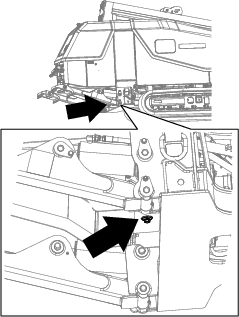
-
Clean the threads on the drain plug and apply 3 layers of PTFE sealing tape.
-
Drain the hydraulic fluid into the container.
Important: The capacity of the hydraulic-fluid tank is 102 L (27 US gallons), so ensure that you have a container of at least 114 L (30 US gallons).
-
Install the drain plug when the hydraulic fluid stops draining.
-
Clean the area around the filter mounting areas.
-
Place a drain pan under the filter and remove the filter (Figure 112).
-
Lubricate the filter gasket of each new filter and fill them with hydraulic fluid.
-
Screw the filters on until the gaskets contact the mounting plates; then tighten the filter an additional 1/2 turn.
-
Fill the reservoir with hydraulic fluid.
Important: Use only the hydraulic fluids specified. Other fluids could cause system damage.
-
Install the reservoir cap.
-
Start the engine and use all of the hydraulic controls to distribute hydraulic fluid throughout the system. Check for leaks; then shut off the engine.
-
Check the fluid level and add enough to raise the level to the Full mark on the dipstick. Do not overfill.
Checking the Hydraulic Lines and Hoses
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 2 years |
|
Inspect the hydraulic lines and hoses daily for leaks, kinked lines, loose mounting supports, wear, loose fittings, weather deterioration, and chemical deterioration. Make all necessary repairs before operating.
Warning
Hydraulic fluid escaping under pressure can penetrate skin and cause injury.
-
Make sure that all hydraulic fluid hoses and lines are in good condition and all hydraulic connections and fittings are tight before applying pressure to the hydraulic system.
-
Keep your body and hands away from pin hole leaks or nozzles that eject high pressure hydraulic fluid.
-
Use cardboard or paper to find hydraulic leaks.
-
Safely relieve all pressure in the hydraulic system before performing any work on the hydraulic system.
-
Seek immediate medical attention if fluid is injected into skin.
Hydraulic System Test Ports
The test ports are used to test the pressure in the hydraulic circuits. Contact your Authorized Service Dealer for assistance.
Drilling-fluid Pump Maintenance
Servicing the Drilling-Fluid-Pump Oil
The drilling-fluid pump is shipped with oil in the crankcase; however, check the oil level before and after you first start the engine.
The crankcase capacity is 1.9 L (2 US qt).
Use only high-quality engine oil that meets the following specifications:
-
API Classification Level Required: CH-4, CI-4 or higher
-
Oil: SAE 30-weight, non-detergent oil above 0° C (32° F)
Toro Premium Engine Oil is available from your dealer. See the parts catalog for part numbers. Also, refer to the engine owners manual, included with the machine, for further recommendations.
Checking the Drilling-Fluid-Pump Oil Level
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the rear hood.
-
Remove the oil dipstick (Figure 116).
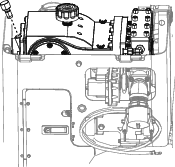
-
Ensure that the oil is at the oil-fill line as shown in Figure 116.
Note: If the oil is below the oil-fill line, refer to step 8 of Changing the Drilling-Fluid Pump Oil and add the necessary amount of oil.
Changing the Drilling-Fluid Pump Oil
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 400 hours |
|
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Open the rear hood.
-
Allow the engine to cool.
-
Remove the drain plug and place a drain pan under the drain-plug hole (Figure 117).
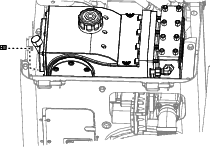
-
Clean the threads on the drain plug and apply 3 layers of PTFE sealing tape.
-
Allow all of the oil to drain into the oil pan (Figure 117).
-
Install the drain plug.
-
Remove the oil-filler cap (Figure 117) and add approximately 1.9 L (2 US qt) of oil, or until the oil reaches the oil-fill line on the dipstick as shown in Figure 116.
Preparing the Drilling-Fluid System for Cold Weather
Prepare the machine as follows after drilling if the temperature will be below 0° C (32° F).
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
Prepare the machine to circulate the antifreeze as follows:
-
Open the rear hood.
-
Place a drain pan under the drill spindle for the leaked antifreeze (Figure 118).
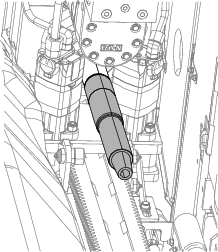
-
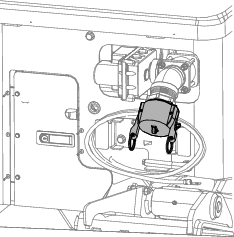
Ensure that the cap is installed on the drilling-fluid pump inlet (Figure 119).
-
Remove the cap from the antifreeze tank for the drilling-fluid pump (Figure 120).
-
Ensure that the tank is full of antifreeze (Figure 120).
-
-
Circulate the antifreeze as follows:
-
Turn the machine off.
-
Install the cap onto the antifreeze tank (Figure 120).
-
Close the antifreeze valve (Figure 120).
Controls Maintenance
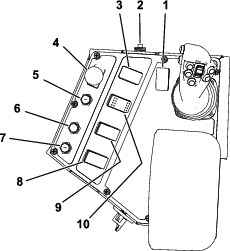
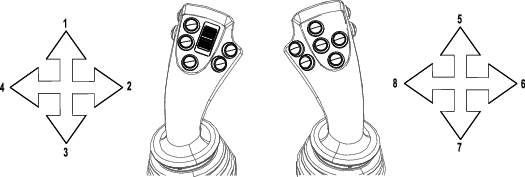
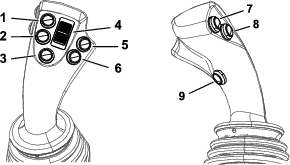
Calibrating the Joysticks and the Travel Pendant
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Every 400 hours |
|
Refer to the joystick section of the Software Guide for this procedure.
Cleaning
Cleaning with the Spray-Hose Attachment
| Maintenance Service Interval | Maintenance Procedure |
|---|---|
| Before each use or daily |
|
The machine comes with a spray-hose attachment that you can use to clean the machine and pipes.
Important: Do not spray any electronic component of the machine and ensure that the hood is down before cleaning the machine with the spray-hose attachment.
Important: If the outside temperature is below freezing, refer to Preparing the Drilling-Fluid System for Cold Weather before cleaning the machine.
To use the spray-hose attachment, perform the following procedure:
-
Move the machine to a level surface, shut off the engine, and remove the key.
-
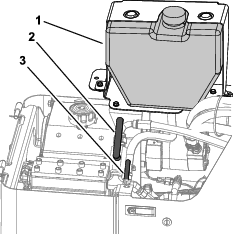
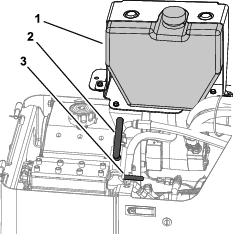
Ensure that the spray-hose attachment switch is in the OFF position (Figure 121).
-
Open the rear hood.
-
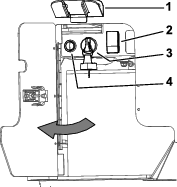
Turn the drilling-fluid valve clockwise to the OFF position (Figure 122).
-
Connect the spray-hose attachment to the fitting (Figure 123).
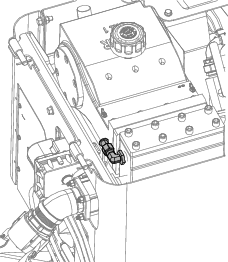
-
Setup up the pump to clean water Connecting to a Drilling-Fluid Source.
Turn the spray-hose attachment switch to the ON position (Figure 122).
-
Turn the drilling-fluid pump to the ON position through the display screen; refer to the Main Drill Functions Displayed in the Pressure Screen in the Software Guide.
-
Using the spray-hose attachment, hold down the lever and spray down the machine and pipes.
Cleaning Plastic and Resin Parts
Avoid using gasoline, kerosene, paint thinner, etc. when cleaning plastic windows, the console, the instrument cluster, the monitor, gauges, etc. Use only water, mild soap, and a soft cloth when you clean these parts.
Using gasoline, kerosene, paint thinner, etc. to clean a plastic or resin part will cause it to discolor, crack, or deform.


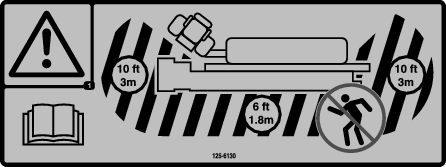

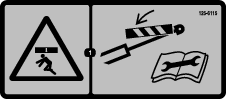
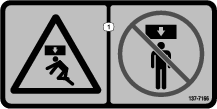



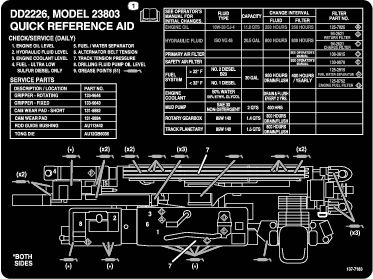


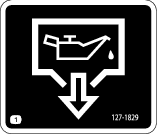


 is displayed on the display,
a regeneration is requested.
is displayed on the display,
a regeneration is requested. is displayed on the display,
a recovery regeneration is requested.
is displayed on the display,
a recovery regeneration is requested.