Maintenance
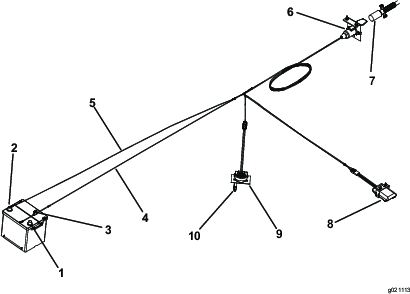
Note: Download a free copy of the schematic by visiting www.Toro.com and searching for your machine from the Manuals link on the home page.
Maintenance Safety
-
Before servicing or adjusting the machine, stop the machine, shut off the engine, engage the parking brake, remove the key, and wait for all moving parts to stop.
-
Perform only those maintenance instructions described in this manual. If major repairs are ever needed or assistance is desired, contact an authorized Toro distributor.
-
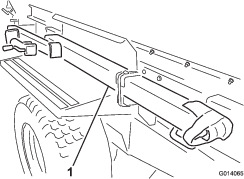
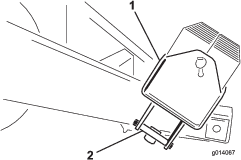
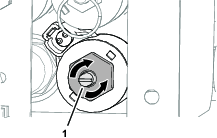
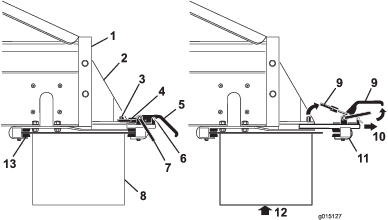
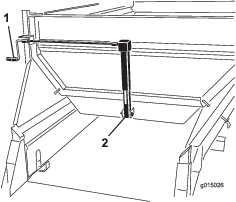
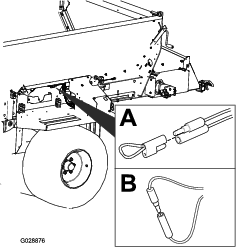
Before doing any maintenance work under the hopper, install the hydraulic cylinder supports.
-
Ensure that the machine is in safe operating condition by keeping nuts, bolts, and screws tight.
-
If possible, do not perform maintenance while the engine is running. Keep away from moving parts.
-
Do not check or adjust the chain tension when the tow vehicle engine is running.
-
Carefully release pressure from components with stored energy.
-
Support the machine with blocks or jack stands when working beneath it.
-
After maintaining or adjusting the machine, ensure that all guards are installed.
Pre-Maintenance Procedures
Warning
Disconnect all power sources to the machine before doing maintenance work.
Warning
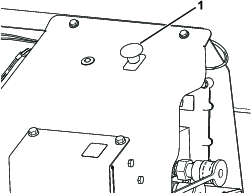
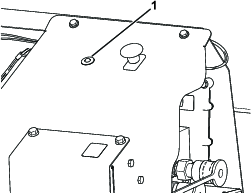
Install the hydraulic cylinder supports before doing any maintenance work under the hopper (Figure 52).
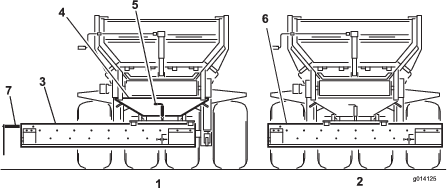
Lubrication
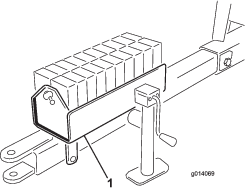
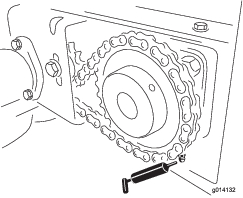
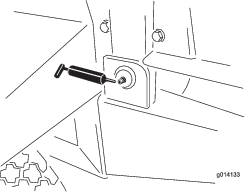
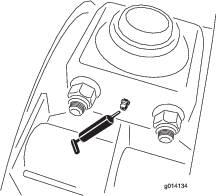
The machine has grease fittings that must be lubricated regularly with No. 2 lithium grease. If the machine is operated under normal conditions, lubricate all bearings and bushings after every 50 hours of operation. Bearings and bushings must be lubricated daily when operating conditions are extremely dusty and dirty. Dusty and dirty operating conditions could cause dirt to get into the bearings and bushings, resulting in accelerated wear. Lubricate grease fittings immediately after every washing, regardless of the interval specified.
-
Wipe the grease fitting clean so foreign matter cannot be forced into the bearing or bushing.
-
Pump grease into the bearing or bushing.
-
Wipe up any excess grease.
The bearing and bushing lubrication points are as follows:
Safety Checks
At the start of each day, complete these safety checks before operating the machine. Report any safety problems to your supervisor. See the Safety Instructions in this manual for details.
Note: Photocopy these pages and use them as a regular safety checklist
Tires and Wheels
-
The recommended tire pressure is 172 kPa (25 psi) for 84 cm (33 inch) tires and 207 kPa (30 psi) for 81 cm (32 inch) tires, or as recommended by the tire manufacturer.
-
Check for excessive wear or visible damage.
-
Check that the wheel bolts are tight and none are missing.
Rear Gate
-
Check that the rear gate closes and latches securely.
-
Check that the adjustable section of the rear gate opens and closes without sticking.
Hitch, Jack, and Rear Jack Leg
-
Check that the hitch pin and jacks are not damaged, and the safety pins are in place. (Replace missing or damaged safety pins.)
-
Check that the hitch connections are not loose. (If so, install a spacer between the hitch connections.)
-
Safely stow all jacks in the up position before traveling.
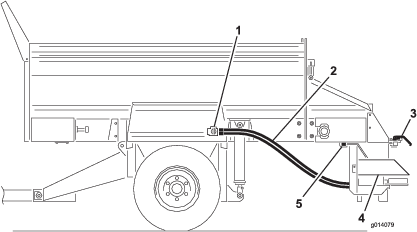
Hydraulic System
-
Check the hydraulic system for oil leaks. If you find a leak, tighten the fitting, or replace or repair the damaged part.
-
Check the hydraulic hoses for wear or visible damage.
-
Check the hydraulic oil level. Fill up if necessary.
Conveyor Belt and Rollers
-
Once a week, check that the conveyor belt is tracking straight on the rollers and does not slip. Make adjustments if required.
-
Every 4 months, check that the idler rollers between the front and rear rollers are not bent or seized. Replace or repair if required.
Belt and Rear Gate Seals
Check all rubber seals for wear or damage. Replace or repair the seals if any leakage occurs.
Options
-
Check that the quick attach brackets are securely locked into place and that the safety clips are installed. Replace missing safety clips.
-
Check that the option is securely clamped and does not move or slide out. Adjust clamps if required.
-
Check the paddles on the Twin Spinner disks for wear. Replace them when they wear thin.
-
Check the Twin Spinner housing for signs of cracking or corrosion.
Safety Decals
Check that the safety decals are undamaged and legible, otherwise replace them.
Electric Brakes
-
Once a month, conduct a simple visual inspection of your brake shoes and linings.
-
Inspect and service your electric brakes once a year.
Hydraulic System Safety
-
Ensure that all hydraulic-fluid hoses and lines are in good condition and all hydraulic connections and fittings are tight before applying pressure to the hydraulic system.
-
Seek immediate medical attention if fluid is injected into skin. Injected fluid must be surgically removed within a few hours by a doctor.
-
Keep your body and hands away from pinhole leaks or nozzles that eject high-pressure hydraulic fluid.
-
Use cardboard or paper to find hydraulic leaks.
-
Safely relieve all pressure in the hydraulic system before performing any work on the hydraulic system.
Hydraulic System Maintenance
The machine is shipped from the factory filled with high quality hydraulic fluid. Check the level of hydraulic oil before the machine is first started and daily thereafter. The recommended replacement oil is as follows:
| Toro Premium Transmission/Hydraulic Tractor Fluid (Available in 5 gallon pails or 55 gallon drums. See parts catalog or Toro distributor for part numbers.) |
Alternate fluids: If the Toro fluid is not available, other petroleum-based Universal Tractor Hydraulic Fluids (UTHF) may be used provided its specifications fall within the listed range for all the following material properties and it meets industry standards. We do not recommend the use of synthetic fluid. Consult with your lubricant distributor to identify a satisfactory product.
Note: Toro will not assume responsibility for damage caused by improper substitutions, so use only products from reputable manufacturers who will stand behind their recommendation.
| Material Properties: | |||
| Viscosity, ASTM D445 | cSt @ 40°C 55 to 62 | ||
| Viscosity Index ASTM D2270 | 140 to 152 | ||
| cSt @ 100°C 9.1 to 9.8 | |||
| Pour Point, ASTM D97 | -35°F to -46°F | ||
| Industry Specifications: | |||
| API GL-4, AGCO Powerfluid 821 XL, Ford New Holland FNHA-2-C-201.00, Kubota UDT, John Deere J20C, Vickers 35VQ25, and Volvo WB-101/BM | |||
Changing Tires
Changing an Outside Tire
-
Keep the machine attached to the tow vehicle, remove any options, and apply the emergency brake.
-
Remove all material from the hopper.
-
Block the tires on the opposite side of the flat tire.
-
Loosen the 6 wheel bolts on the flat tire with a lug wrench, but do not remove them.
-
Hoist or jack the machine until the tire is off the floor or ground. Ensure that the machine is stable.
-
Remove the loose wheel bolts and remove the tire.
-
Repair the damaged tire.
-
Install the tire onto the machine by reversing the above steps.
Note: Ensure that the wheel is centered on the hub and all 6 wheel bolts are tight. Torque in a crossover pattern to 135 N-m (100 ft-lb).
Changing an Inside Tire
-
Keep the machine attached to the tow vehicle, remove any options, and apply the emergency brake.
-
Remove all material from the hopper.
-
Block the tires on the opposite side of the flat tire.
-
On the side with the tire to be changed, remove the 4 bolts holding the walking beam suspension's bearings to the chassis. (Loosen but do not remove the outside wheel nuts to give more clearance for bearing bolts).
-
Hoist or jack the machine until the inside tire and walking beam axle assembly can be rolled out from underneath. Ensure that the machine is stable.
-
Remove the tire.
-
Repair the damaged tire.
-
Install the tire onto the machine by reversing the above steps.
Note: Ensure that the wheel is centered on the hub and all 6 wheel bolts and the bearing bolts are tight to 135 N-m (100 ft-lb).
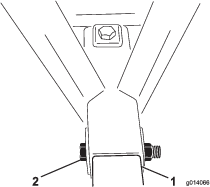
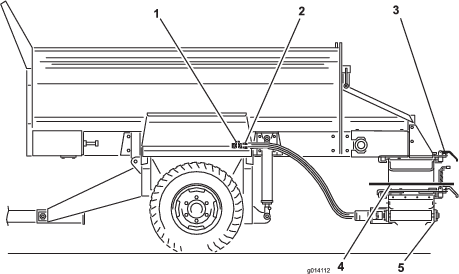
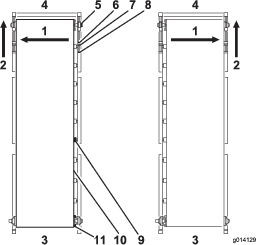
Tracking the Conveyor Belt
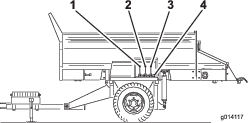
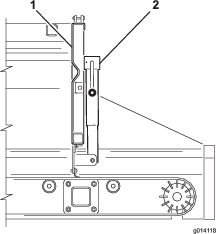
If the conveyor belt is not centered and tracks to 1 side, it needs to be adjusted (Figure 57). The best time to do this is between loads during operation.
-
Go to the rear of the machine and determine which side of the belt is touching.
-
Go to the front on the same side, loosen the locking nut, and tighten the adjuster nut by 1 quarter turn.
-
Tighten both locking nuts before running the machine.
-
Load the machine with material and run the load through until empty. Repeat multiple times.
-
Stop the belt and go to the rear of the machine to observe the results.
You may need to repeat the above steps several times until the belt begins to move and track properly.
Note: The belt may move slightly depending on the type of load and its position. If the belt is not touching the side rails, you do not need to track the belt.
Important: Do not adjust the rear drive roller of the belt. It is set to factory specifications. Contact your authorized Toro distributor if adjustment is required.
Tensioning the Conveyor Belt
Check and adjust the belt tension frequently (Figure 57). All rubber conveyor belts will stretch, especially when they are new or have not been used recently.
-
Park the machine on level ground with the rear gate and feed gate at least 6.25 mm (1/4 inch) off the floor (depending on the material).
-
Fully load the machine with sand that you expect the machine to use.
-
Remove the black front covers on either side of the machine.
-
Using 2 wrenches, hold the end of the tensioner rod stationary, while loosening the locking nut closest to the end of the rod.
-
Move the locking nut back 2–5 cm (1–2 inches).
Warning
Use extreme caution around moving parts with safety guards removed.
-
Turn on the conveyor belt.
-
If belt slips, tighten the tension bolts evenly (with machine off) half a turn and check again. Continue until the belt moves without any slippage.
-
Give both tensioning bolts another half turn. At this point you should have proper tension.
-
To verify, look underneath at the chassis cross member. The middle of the belt should just clear the chassis cross member when the machine is in the down position. If the middle of the belt is touching the cross member, tighten both tensioning bolts another quarter of a turn.
Important: Be patient. Do not over-tension the belt.
Important: Do not use air tools on the belt tensioning bolts.
Changing the Conveyor Belt
Read these instructions before removing the belt. If the belt is completely destroyed, simply use a knife to cut the belt in an undamaged area. If you intend to make a warranty claim, the belt supplier must inspect the belt to evaluate the damage and make recommendations for replacement.
Removing the Belt
-
Remove the black safety covers located on the 4 outer corners of the machine.
-
Remove the guides for the inner rubber liner from the front and both sides of the hopper, with the metal rails attached.
-
Remove the silicone sealer on the rear of the metal rails (but remember to apply the silicone sealer when installing them).
-
At both front corners, use 2 wrenches to hold the end of the tensioner rod stationary.
-
Loosen the nut closest to the end of the tensioning rod.
-
Move the inside adjusting nut back until the tensioning rod clears the pillow block bearing.
Note: The front idler roller is supported by 2 pillow block bearings sitting in an upper and lower guide (1 set on each side of the machine).
-
Support the front idler roller.
-
Go to the right front corner and remove the locking collar that holds the pillow block bearing on the shaft. Do this by backing off the set screws and turning the locking collar counterclockwise. Using a hammer and punch, tap the locking collar counterclockwise until it releases from the shaft.
-
Repeat this step for the left front corner.
-
Remove the pillow block bearings by sliding the idler roller back so the pillow block bearings slide out of their guides.
-
Remove the 2 safety brackets and slide the roller down through the open hole.
-
Go to the rear of the machine and loosen the tensioning sprocket.
-
Remove the chain from the drive sprocket.
-
Loosen the set screws on the drive sprocket and remove the drive sprocket and key from the drive roller shaft.
-
Support the rear drive roller.
Important: Do not disturb the rear roller adjustment bracket assembly. It is designed to adjust the rear roller automatically if the belt is not tracking accurately
-
Remove the 4 bolts in the flange bearings on both sides.
-
Remove the locking collars next to the flange bearings on the shaft, and slide both bearings off the shaft.
-
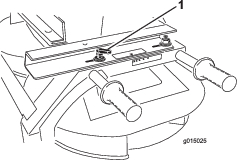
Remove the 2 option attachment brackets (Figure 58).
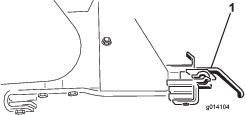
-
Lower the drive roller down through the slots.
-
Remove the rear gate for a better view.
-
Note the position of the cartridge inside the hopper, so that you can install it in the same position and direction. It is bolted in 6 places along the side of the machine (3 bolt plates on each side).
-
Secure the cartridge by using straps from a lifting device on each of the 4 corners.
-
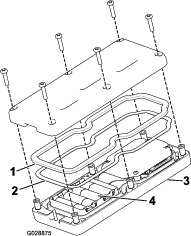
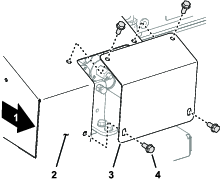
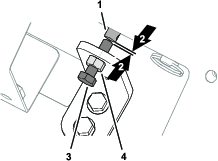
Remove the 24 bolts to release the cartridge (Figure 59).
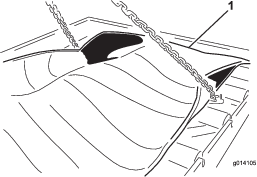
-
Remove the cartridge by lifting it out from the top of the machine. Place it on the ground (Figure 60).
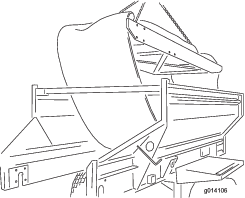
Installing the Belt
To install a new belt, reverse the above instructions, but keep in mind the following important notes and instructions.
Important: The conveyor belt is designed to work primarily in 1 direction. Ensure that the painted arrow in the middle of the belt is pointing towards the rear of the machine (looking down from above).
Note: Before sliding the rear drive roller back up through the slot and into place, ensure that you have already installed the 4 bolts (from the inside facing out) for connecting the pillow block bearings. Otherwise, you will have to remove the drive roller to gain enough clearance to install these bolts.
When installing the rear drive roller, ensure that the shaft connecting to the motor is on the left side. It has a keyhole cut into it for securing the drive sprocket.
Before applying tension with the tensioner rods at the front of the machine, use your hands to manually center the belt at the front and rear.
Track and tension the belt by following the instructions in the Maintenance Section of the manual.
The front idler and rear drive rollers provide excellent traction for pulling the belt under load, so do not overtighten or stretch the belt.
Apply silicone sealer to the rear side of the metal rails and at the 2 front corners of the floor where the rails meet. The sealer deflects any material from getting past the rails.
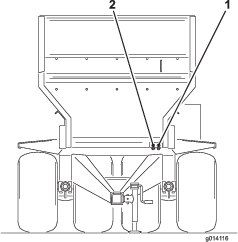
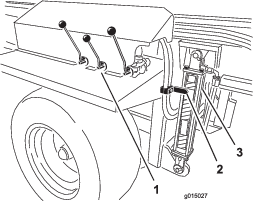
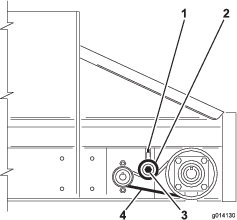
Adjusting the Conveyor Drive Chain
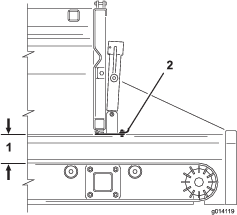
If the conveyor drive chain is loose, it needs to be tightened (Figure 61).
-
Shut off the engine of the tow vehicle and engage the parking brake.
-
Remove the rear conveyor drive guard.
-
Loosen the bolt that goes through the tensioner sprocket.
-
Tighten the positive locking screw using moderate force.
-
Tighten the tensioner sprocket bolt.
-
Check that the chain is sufficiently lubricated, and that the sprockets are secure to the shafts.
-
Replace the rear conveyor drive guard.
Caution
Do not over tension the chain. Leave just enough tension to take up the extra slack.
Maintaining the Electric Brakes
Inspecting the Electric Brakes
Once a month, conduct a simple visual inspection of your brake shoes and linings.
Inspect and service your electric brakes once a year.
Adjusting the Electric Brakes
Adjust the electric brakes after the first 3 months of operation, or sooner depending on use or performance.
-
Jack up the machine securely.
-
Ensure that the wheel and drum rotate freely.
-
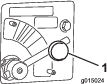
Remove the adjusting hole cover from the slot on the bottom of the brake backing plate.
-
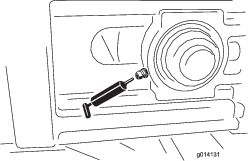
With a screwdriver, rotate the star wheel of the adjuster assembly to expand the brake shoes (Figure 62).
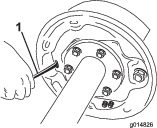
-
Adjust the brake shoes out until the pressure of the linings against the drum makes the wheel difficult to turn.
-
Rotate the star wheel in the opposite direction until the wheel turns freely with a slight drag on the lining.
-
Replace the adjusting hole cover.
-
Repeat the above procedure on each brake.
Inspecting the Brake Shoes and Linings
Once a month, conduct a simple visual inspection of your brake shoes and linings.
When a brake shoe becomes worn, replace both shoes on each brake, and both brakes on the same axle. This ensures that the brakes remain balanced.
Replace the brake linings when they are
-
worn to 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) or less remaining thickness
-
contaminated with grease or oil
-
abnormally scored or gouged
Note: Hairline heat cracks are normal in the brake linings and should not cause concern.
Yearly Brake Cleaning and Inspection
Inspect and service your electric brakes once a year or more often with heavy use or declining performance
-
Change magnets and shoes when they become worn or scored.
-
Clean the backing plate, magnet arm, magnet, and brake shoes with an automotive brake cleaner.
-
Ensure that all parts removed are replaced in the same brake and drum assembly that they were removed from.
-
Inspect the magnet arm for any loose or worn parts.
-
Check the shoe return springs, the hold down springs, and the adjuster springs for stretch or deformation and replace them if required.
Caution
Brake dust can be hazardous to your health if inhaled, take precautions when servicing brakes:
-
Do not create or breathe dust.
-
Do not machine, file, or grind the brake linings.
-
Do not use compressed air or dry brushing for cleaning.
-
Brake Lubrication
Before reassembling the electric brakes, apply a light film of anti-seize compound, or grease such as “Lubriplate,” on the:
-
brake anchor pin
-
actuating arm bushing and pin
-
areas on the backing plate that are in contact with the brake shoes and magnet lever arm
-
actuating block on the actuating arm
Important: Do not allow grease to contact the brake linings, drums, or magnets.
Inspecting the Magnets
The brakes’ electromagnets are designed to provide the proper input force and friction.
Inspect the magnets regularly, and replace if they become unevenly worn. Use a tool with a straight edge to check wear.
Even if the wear is normal, you should replace the magnets if any part of the magnet coil is visible through the friction material on the magnet face. Replace the magnets in pairs (both sides of an axle).
When replacing the magnets, also resurface the drum armature surface.





 , which means Caution, Warning,
or Danger—personal safety instruction. Failure to comply with
these instructions may result in personal injury or death.
, which means Caution, Warning,
or Danger—personal safety instruction. Failure to comply with
these instructions may result in personal injury or death.